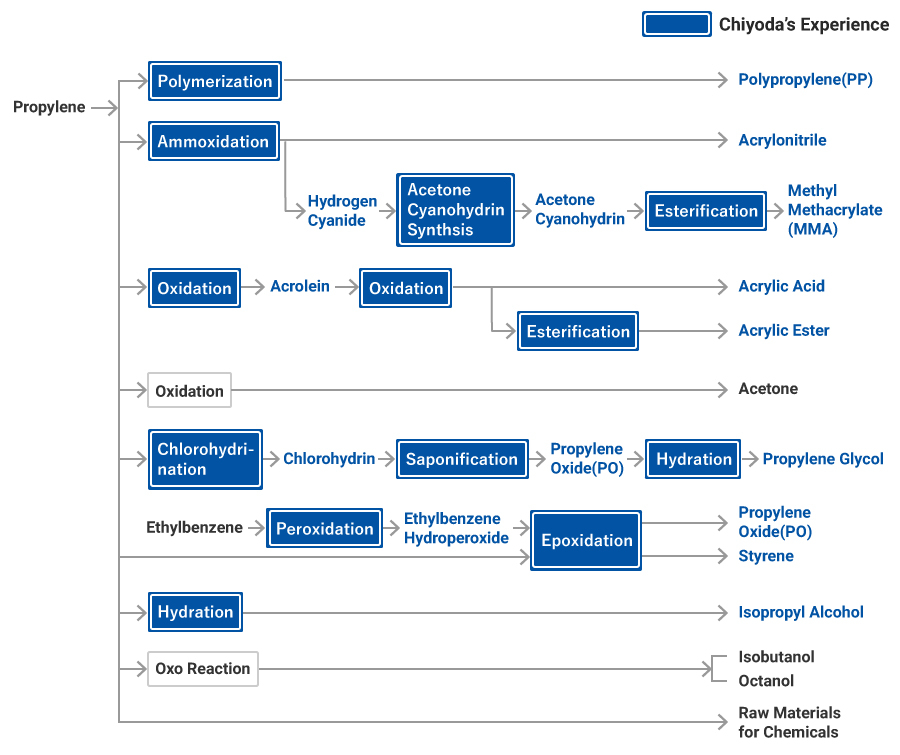
Propylene and Its Derivatives
Propylene has a double bond with three carbons and is used to produce polypropylene resin, acrylonitrile, acrylic acid, propylene oxide, isopropyl alcohol, and acetone through polymerization, oxidation, alkylation, hydration and the addition of halogen. Propylene is as important a basic chemical in the petrochemical industry as ethylene.
[ Propylene and Its Derivatives ]
Capabilities
Polypropylene Process
Polypropylene is applied to a variety of fields for its relatively low cost and excellent rigidity, heat resistance and gloss.
It is polymerized largely in four ways: solution polymerization, suspension polymerization, bulk polymerization, and gas-phase polymerization.
Propylene Oxide (PO) Process
The process of direct oxidation of propylene to produce propylene oxide is yet to be established. Formerly, propylene oxide was produced by the chlorohydrin process, which produces a large amount of calcium chloride as a by-product. Today, the mainstream process produces propylene oxide from peroxides, such as ethyl benzene, and propylene. This process produces propylene oxide (PO) plus styrene (SM) as a by-product. We construct large-scale SM/PO plants using this process.
Key projects
Chiyoda started polypropylene plant construction using solution polymerization in Japan in the 1960s. We started execution of plant construction projects in foreign countries in the 1980s. We are a core contractor of the gas-phase Innovene process with much experience building polypropylene plants.

