CCS / CCU
Contributing to the Realization of a Decarbonized Society through Solutions for Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage
The adoption of next-generation energy solutions, such as renewable energy and hydrogen, is gaining momentum in line with the accelerating global drive towards decarbonization. Reducing the environmental impact of existing fossil fuels by controlling and utilizing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions is essential to meeting increasing energy demand associated with the economic growth of emerging countries.
Technologies for Carbon dioxide Capture and Storage (CCS), capturing CO2 emitted from industrial activities, or capturing it from the atmosphere, for injection and storage underground, and Carbon dioxide Capture and Utilization (CCU), also known as carbon recycling, effectively utilizing captured CO2 as a resource.
Chiyoda continues to contribute to reducing carbon emissions and associated environmental impacts by providing solutions for CCS and CCU.
CCS
Chiyoda‘s CCS Initiatives
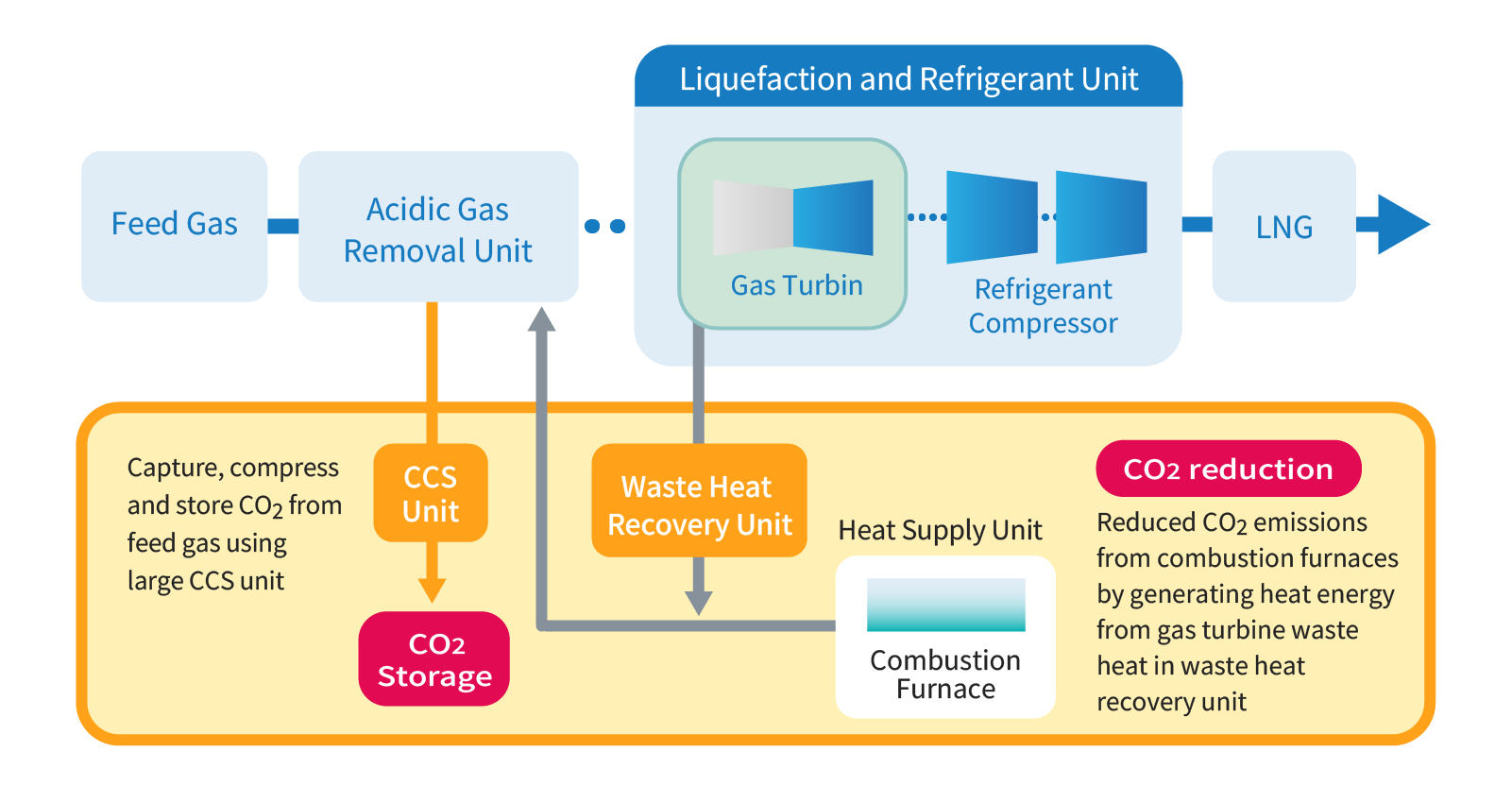
Cleaner LNG plant Construction to Reduce CO2 Emissions
As the global drive towards a decarbonized society accelerates, the demand for environmentally friendly LNG Plants (‘Cleaner LNG Plants’) with reduced CO2 emissions is a major development concept for the LNG industry. Chiyoda has a pioneering track record in the construction of cleaner LNG plants by implementing large-scale CCS facilities to reduce CO2 emissions during operation.
[Conventional LNG Plant]
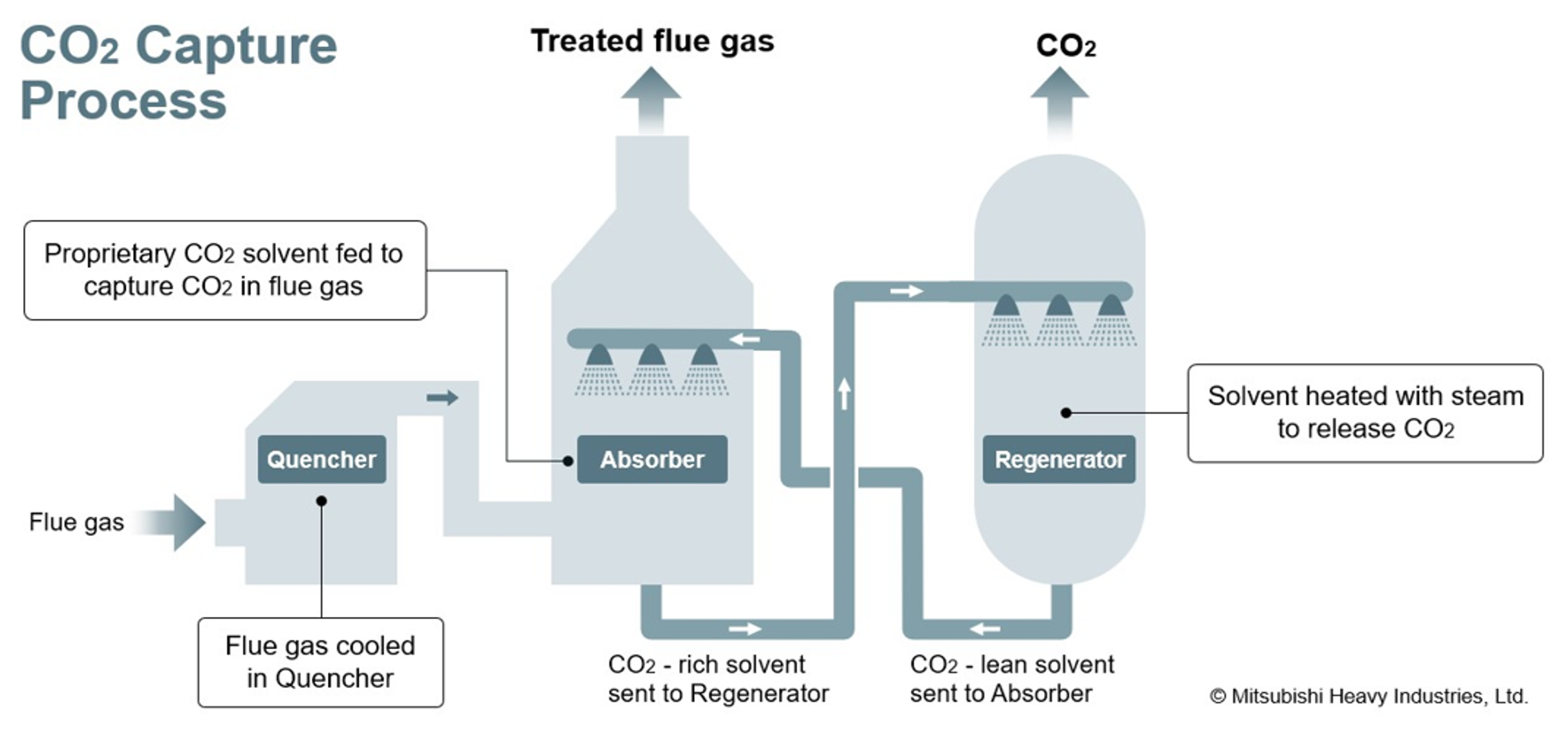
A General Licensing Agreement with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. for CO2 Capture Technologies.
The strategic general licensing agreement with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI) for CO2 capture technologies promotes the licensing of MHI’s CO2 capture technologies, ie: the 'KM CDR ProcessTM' (Kansai Mitsubishi Carbon Dioxide Recovery Process) and the 'Advanced KM CDR ProcessTM' jointly developed with The Kansai Electric Power Co., Inc., to be applied to CO2 capture projects in Japan.
MHI is a leading licensor of CO2 capture technologies, with a track record of delivering CO2 capture plants worldwide. Demand for carbon dioxide capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) is expected to grow in Japan and this partnership builds on our engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) activities, further strengthening Chiyoda’s Japanese CCUS project capabilities.
About MHI Group’s CO2 capture technologies
MHI Group has been developing the 'KM CDR ProcessTM' (Kansai Mitsubishi Carbon Dioxide Recovery Process) and the 'Advanced KM CDR ProcessTM' in collaboration with the Kansai Electric Power Co., Inc. since 1990. As of May 2025, the Company has delivered 18 plants adopting these processes. The 'Advanced KM CDR ProcessTM' adopts the 'KS-21TM' solvent, which incorporates technological improvements over the amine-based 'KS-1TM' and offers superior regeneration efficiency and lower deterioration than the 'KS-1TM', and it has been verified to provide excellent energy saving performance, reduce operation costs, and result in low amine emissions.
Please refer to the flowing link for further information on MHI Group’s CO2 capture plants:
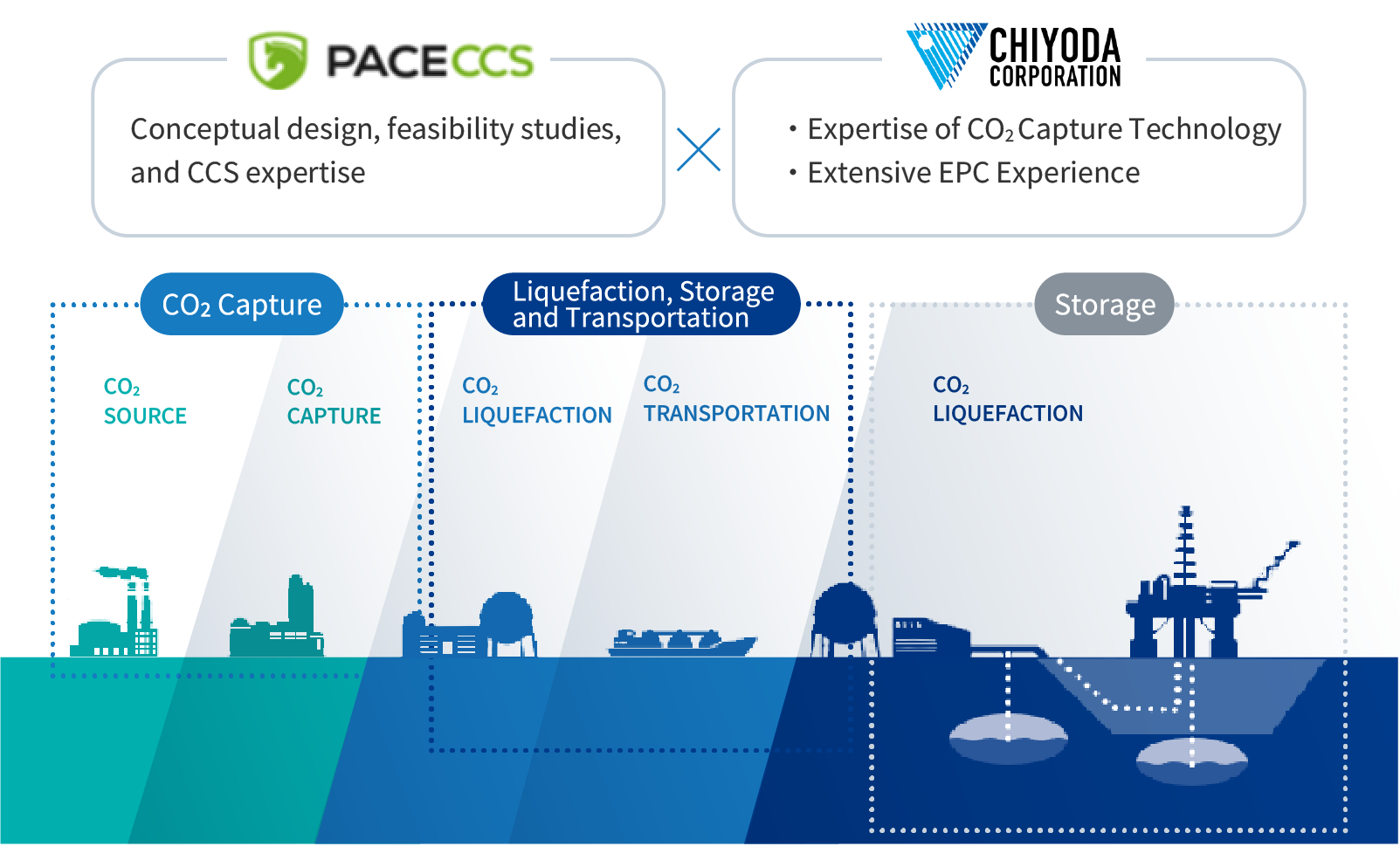
Integrated CCS Value Chain Solutions
Through our collaboration with Pace CCS, a leading global CCS system design company with expertise and experience in upstream design in the CCS field, Chiyoda provides integrated solutions that cover the entire CCS value chain, including CO2 capture, liquefaction, storage, transportation and sequestration.
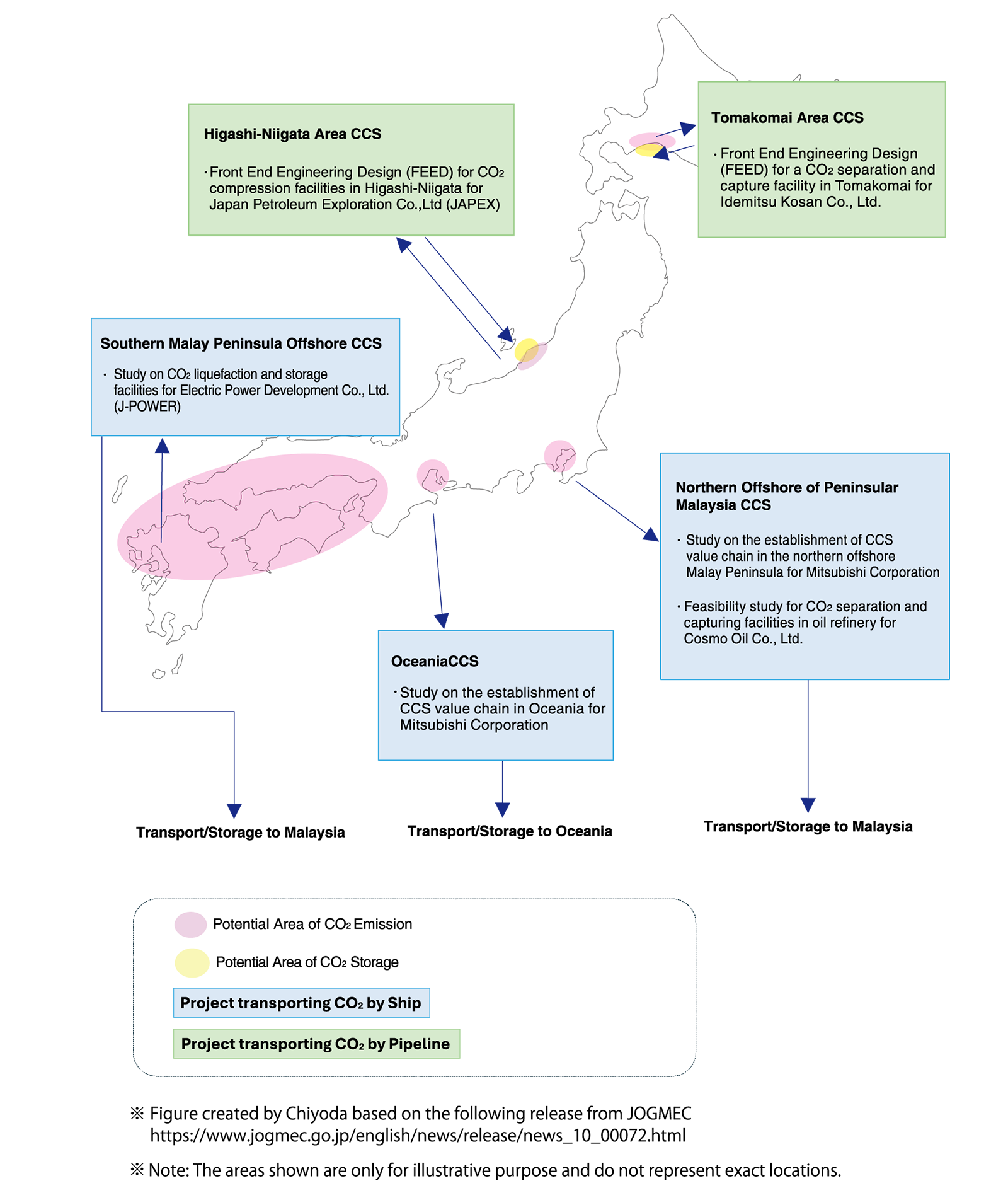
CCS Projects in Japan
Chiyoda is engaged in several CCS projects in Japan.
Video of Chiyoda’s CCS initiatives「CHIYODA x CCS」
CCU
Chiyoda is actively engaged in technology development and demonstration projects related to CCU, utilizing our expertise in scale-up technology and engineering expertise in the oil and gas sector and environmental field, including:
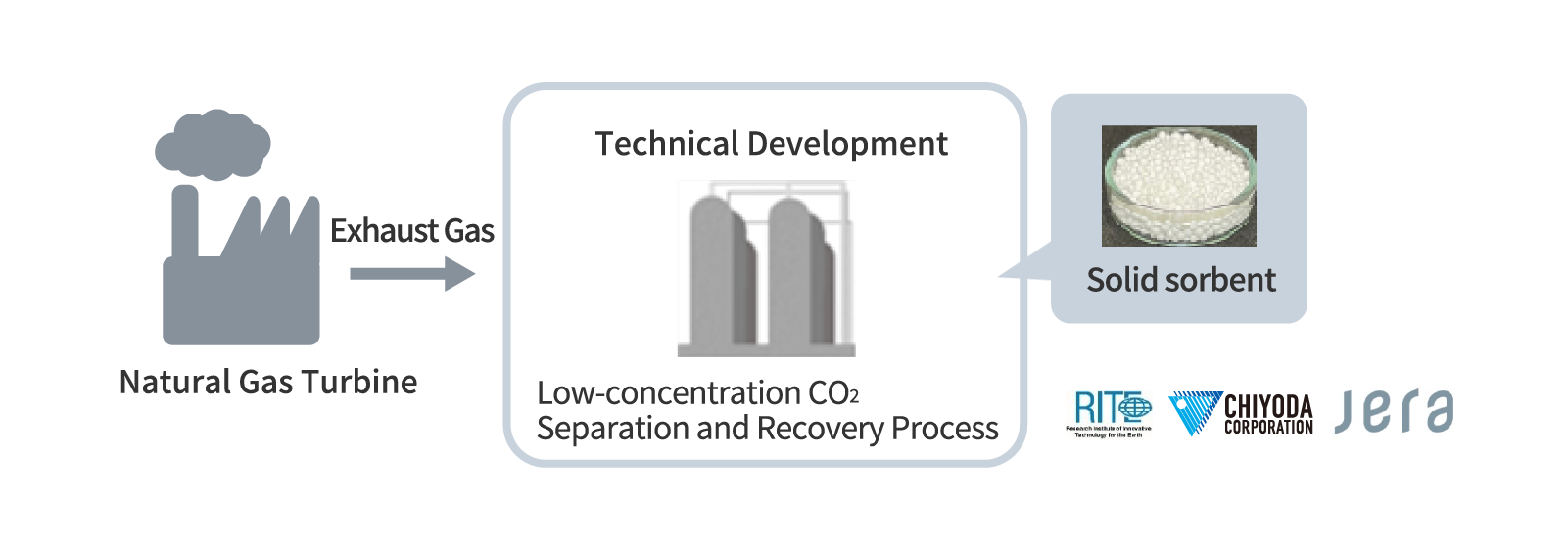
Joint Technology Development centered on Solid Sorbent Materials to Reduce Low-Concentration CO2 Separation and Recovery Costs
As part of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) Green Innovation Fund project (2022-2030) for carbon neutrality in natural gas utilization, Chiyoda is undertaking the development and demonstration of core solid sorbent material technology to reduce costs of the separation and recovery of low-concentration CO2 from gas turbine exhaust gases.
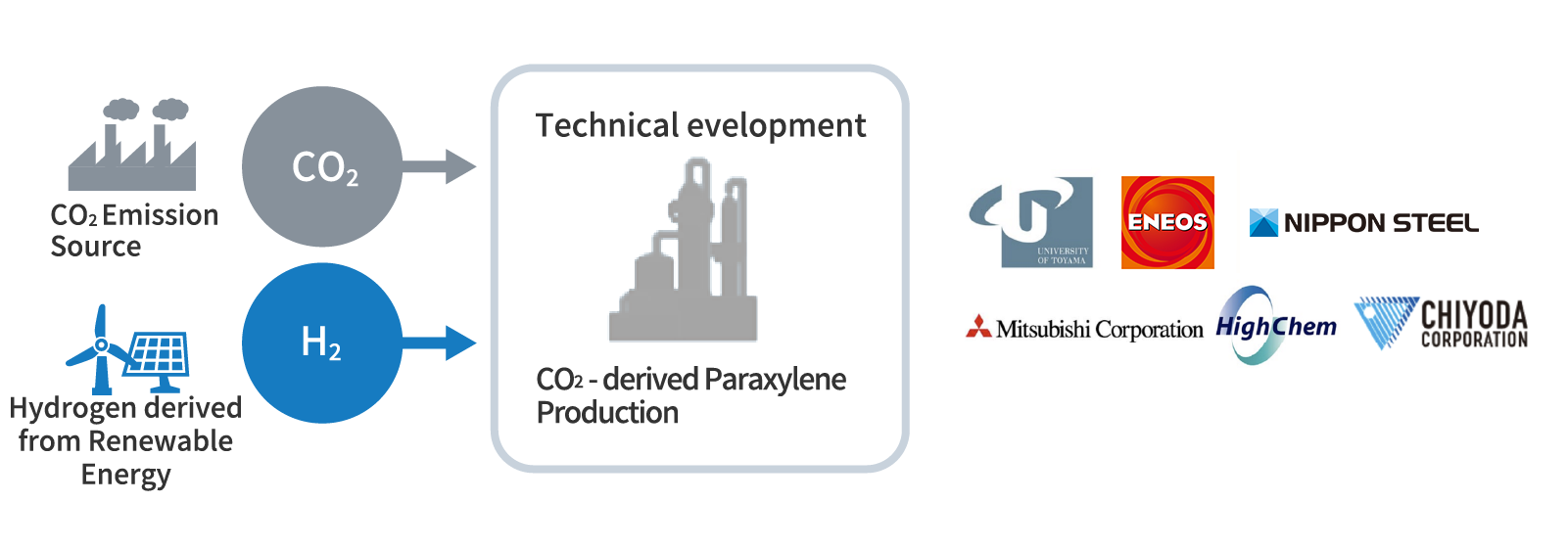
Paraxylene from CO2
As part of a NEDO project(2020-2024) and its subsequent project for the development of CO2 utilization technology in the production of chemicals aimed at replacing existing fossil fuel-derived chemicals, Chiyoda is engaged in cutting-edge technology development to produce paraxylene (a raw material for PET and polyester) using CO2 as a raw material.
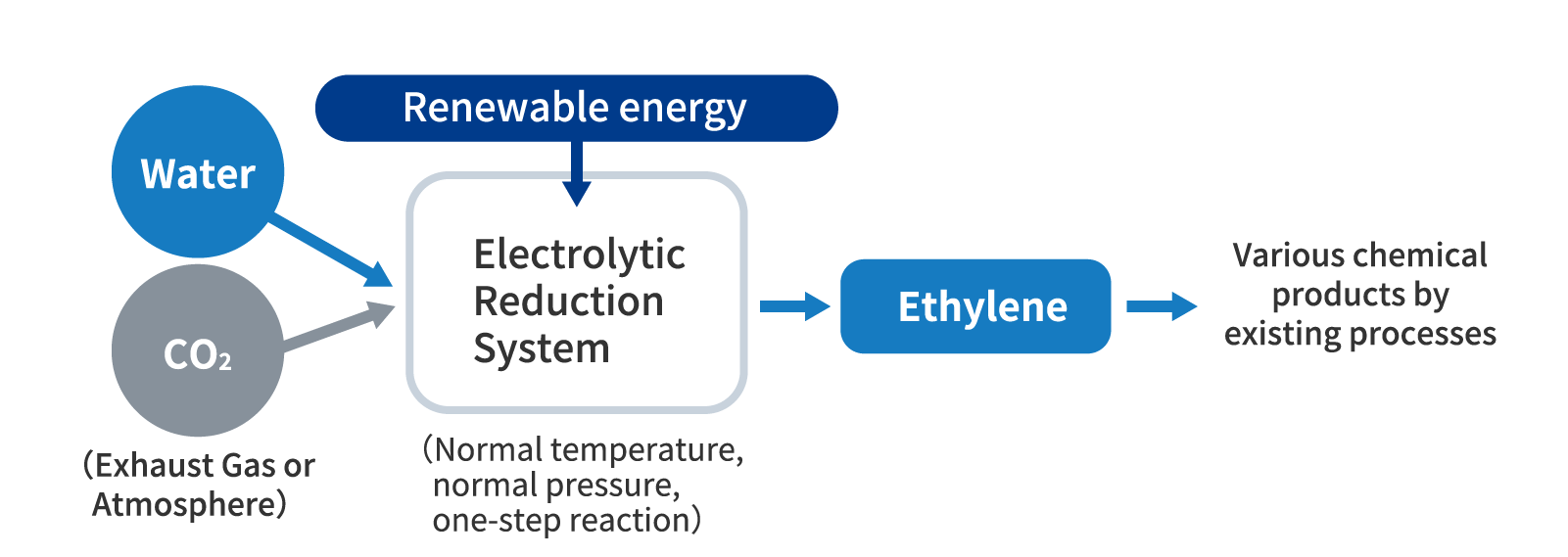
Ethylene (basic chemical) from CO2 and Water
In a collaborative initiative between industry, academia and government as part of the NEDO Moonshot Research and Development Program from FY2020 to FY2029, Chiyoda is engaged in the research, development and demonstration of an innovative large-scale CO2 utilization system, primarily based on electrochemical processes.
Demonstration and Basic Design Projects
Chiyoda is participating in a wide range of projects, including basic design and demonstration and testing facilities, related to the social implementation of decarbonization technologies, and are collaborating with clients from early project stages to expand our expertise and generate new projects.
Major Initiatives
CO2 Methanation Test Plant
Chiyoda is engaged in the design, procurement and construction (EPC) of one of the world’s largest testing facilities with a capacity of 400 Nm3-CO2/h, as part of a technology development project promoted by INPEX Corporation in collaboration with Osaka Gas Co., Ltd. under a subsidy program adopted by NEDO, aimed at the practical application of CO2 methanation systems.
CO2 to CO Conversion Plant
Chiyoda is involved in the basic design of a plant to convert CO2 into carbon monoxide (CO) with an efficiency of over 90%, as part of a project promoted by Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd. This plant will be used for the research and development of ‘Promotion of Carbon Recycling Using CO2 from Bio-manufacturing Technology as a Direct Raw Material”, adopted by NEDO’s Green Innovation Fund program.