LNG Plants
Leading the decarbonization of LNG plants and contributing to a stable supply of clean energy
The Importance of LNG for a Stable Clean Energy Supply and the Transition to Decarbonization
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been converted into a liquid by reducing its temperature to minus162℃, reducing its volume to approximately 1/600th of its gaseous form to facilitate efficient transportation and storage. LNG offers excellent energy supply stability and is commonly used worldwide as a clean energy source, emitting lower quantities of environmental pollutants, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), compared to other fossil fuels. Demand for LNG is expected to steadily increase due to its growing importance in providing a stable supply of clean energy for the economic development of a rising global population and as a transitional energy source for a decarbonized society.
Leveraging Chiyoda’s Experience as a Global Leader in LNG Plant Construction and LNG Value Chain Optimization
The successful construction of LNG plants requires advanced technical expertise and project management capabilities. Since completing our first LNG plant in the UAE in 1976, Chiyoda has participated in the design and construction of LNG plants across the globe, adapting to their ever-increasing complexity, scale and sophistication due to advancements in gas field exploration technology and expanding LNG demand. As an established market leader in LNG plant construction, Chiyoda has contributed to the worldwide stable supply of clean energy, including to Japan, and supported the economic development of gas producing countries.
As gas field exploration technology continues to advance in line with increasing LNG demand, the LNG manufacturing process and its utilization is becoming more diverse. Chiyoda provides optimal solutions for the LNG value chain, including gas development, LNG plants, LNG receiving facilities, regasification and power generation facilities.
Track Record of EPC LNG Plant Projects [as of March 2024]
26 projects,47trains,220 millions ton production capacity/year
| Region | Country | Number of EPC Projects* |
Number of Trains |
Production Capacity (million tons/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle East | Qatar | 8 | 16 | 101.9 |
| Oman | 2 | 3 | 9.9 | |
| U.A.E | 2 | 3 | 4.7 | |
| North America | USA | 4 | 9 | 43.0 |
| Asia, Australia | Indonesia | 5 | 6 | 14.2 |
| Australia | 1 | 2 | 8.9 | |
| Papua New Guinea | 1 | 2 | 6.9 | |
| Europe, Russia | Russia | 2 | 5 | 26.1 |
| Africa | Algeria | 1 | 1 | 4.7 |
| Total | 26 | 47 | 220.3 |
- Including projects under EPC(engineering, procurement, and contruction)
Support for Liquefaction Methodologies
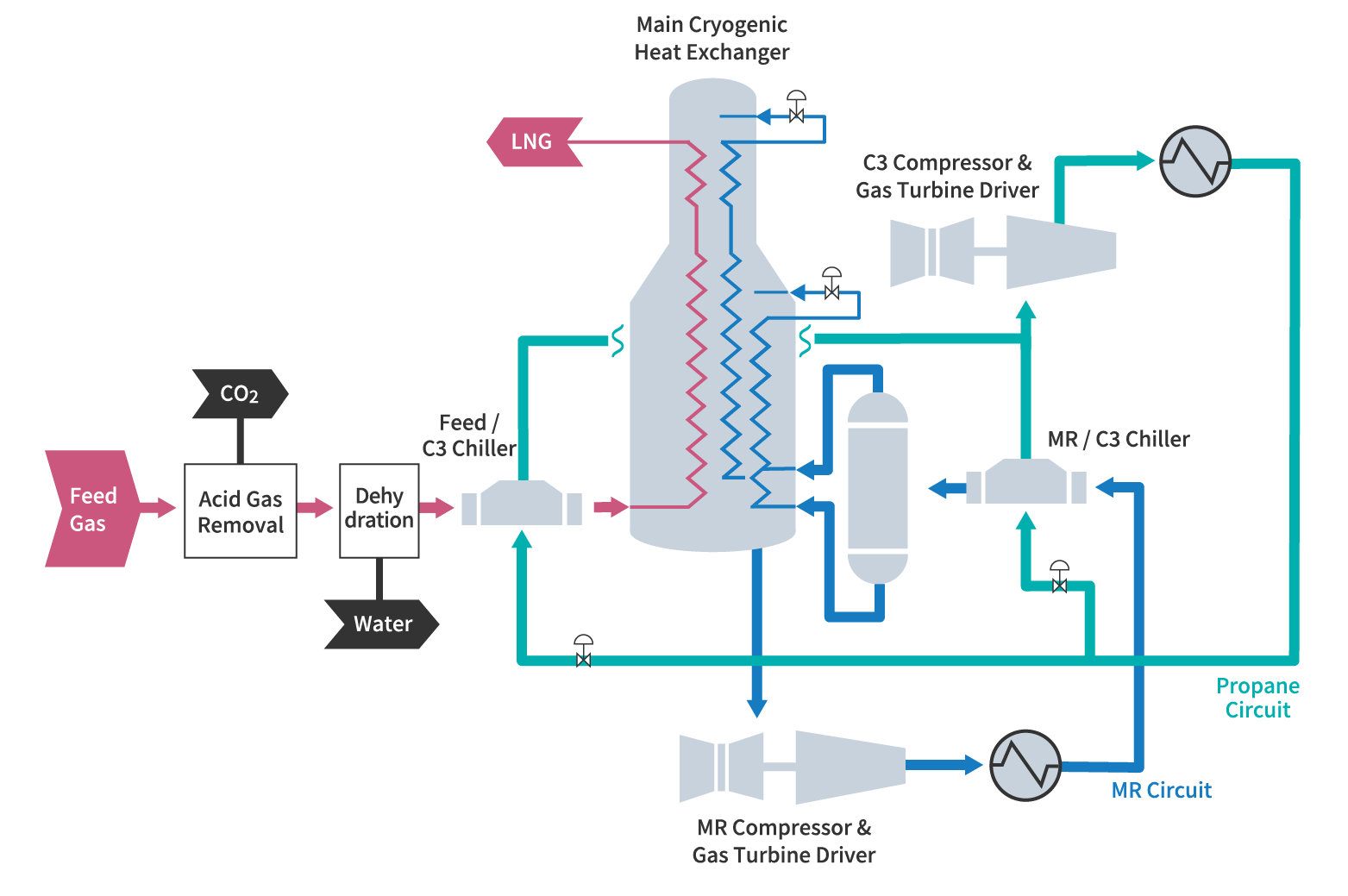
Natural gas is cooled and liquefied in LNG plants using refrigerants through liquefaction processes such as C3-MR, (Propane (C3) pre-cooled Mixed Refrigerant), SMR (Single Mixed Refrigerant), DMR (Dual Mixed Refrigerant) and AP-X. The optimal liquefaction method varies depending on factors such as LNG production volume and construction site conditions. Chiyoda has extensive liquefaction methodology experience, from the evaluation of processes to design and construction.
The natural gas is pre-cooled, condensed and subcooled to form LNG using equipment such as main heat exchangers, refrigeration compressors, drivers and heat exchangers used for refrigerant cooling. In the typical C3-MR process, a mixed refrigerant is used for condensation and subcooling and propane refrigerant is used to pre-cool natural gas and cool the mixed refrigerant. This process involves adjusting the composition of the mixed refrigerant according to the composition of the natural gas to optimize operational efficiency.
General LNG Liquefaction Process
Promote LNG Plants that Contribute to Reducing CO2 Emissions
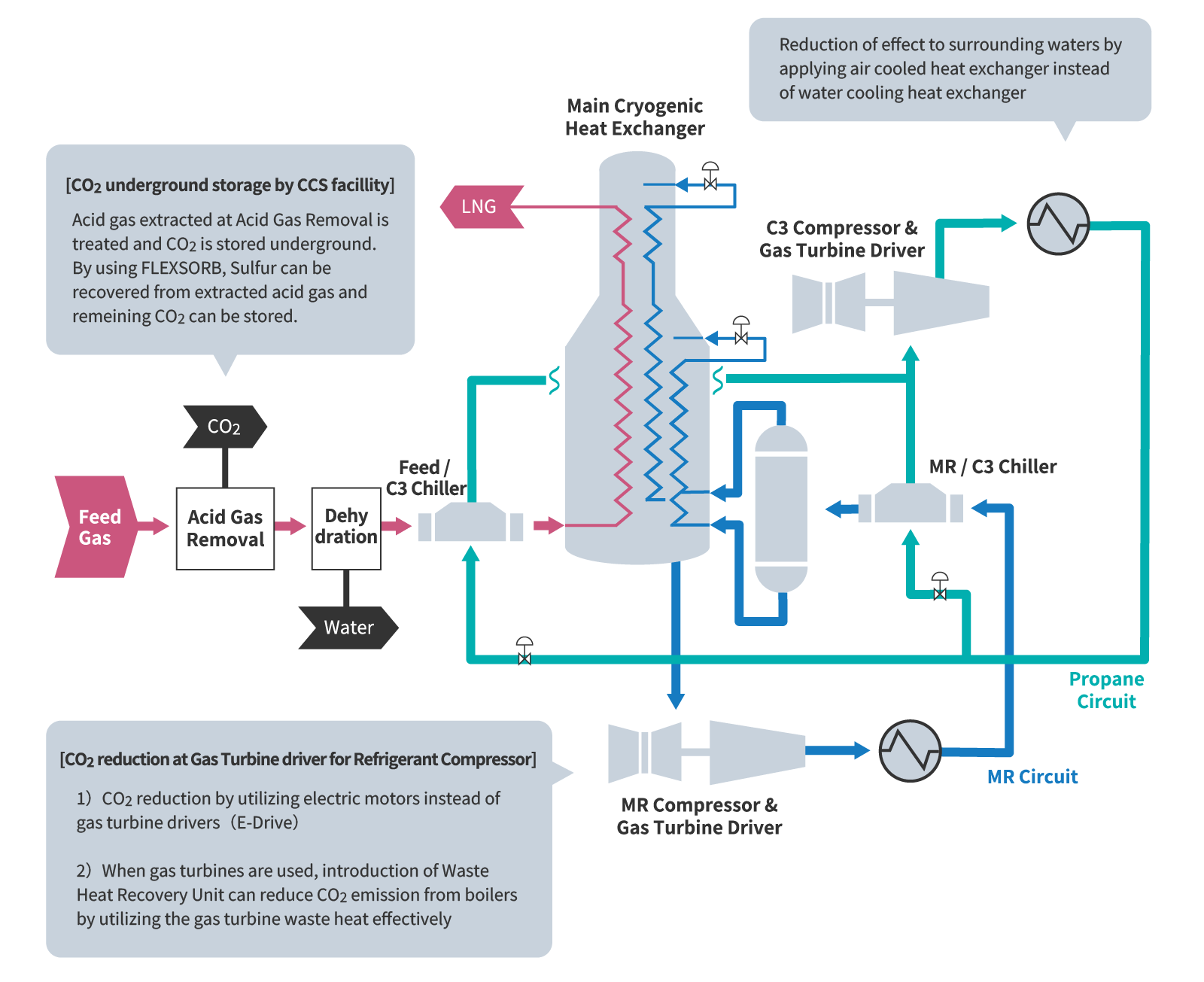
The demand for environmentally friendly LNG Plants (‘Cleaner LNG Plants’), with reduced CO2 emissions as the global drive towards a decarbonized society accelerates, is a major development concept for the LNG industry.
Chiyoda’s pioneering experience in lowering CO2 emissions and reducing environmental impacts during LNG plant operation through the construction of Cleaner LNG Plants, includes large-scale Carbon dioxide Capture and Storage (CCS) facilities, the use of electric motors in gas cooling systems and adopting air-cooled heat exchangers in lieu of water-cooled ones that use seawater.
Chiyoda leverages knowledge gained from these achievements to promote the development of Cleaner LNG Plants by collaborating with customers from the early stage, improving LNG plant efficiency and reliability by designing from a lifecycle perspective, including optimization of operation and maintenance, and contributing a stable supply of cleaner LNG to support decarbonization.
Examples of Major Environmental Impact Reduction Initiatives at LNG Plants
Key Technology
Major Projects
- North Field East (NFE) LNG project, Qatar
-
- The world's largest ‘Cleaner LNG Plant’ with large-scale CCS and waste heat recovery facilities
- Freeport LNG project, USA
-
- A ‘Cleaner LNG Plant’ with an electric motor-driven (E-Drive) gas cooling system
- Ichthys Onshore LNG Facilities Project (Train 1, 2), Australia
-
- A large-scale LNG project operated by INPEX corporation, the first for a Japanese company.
