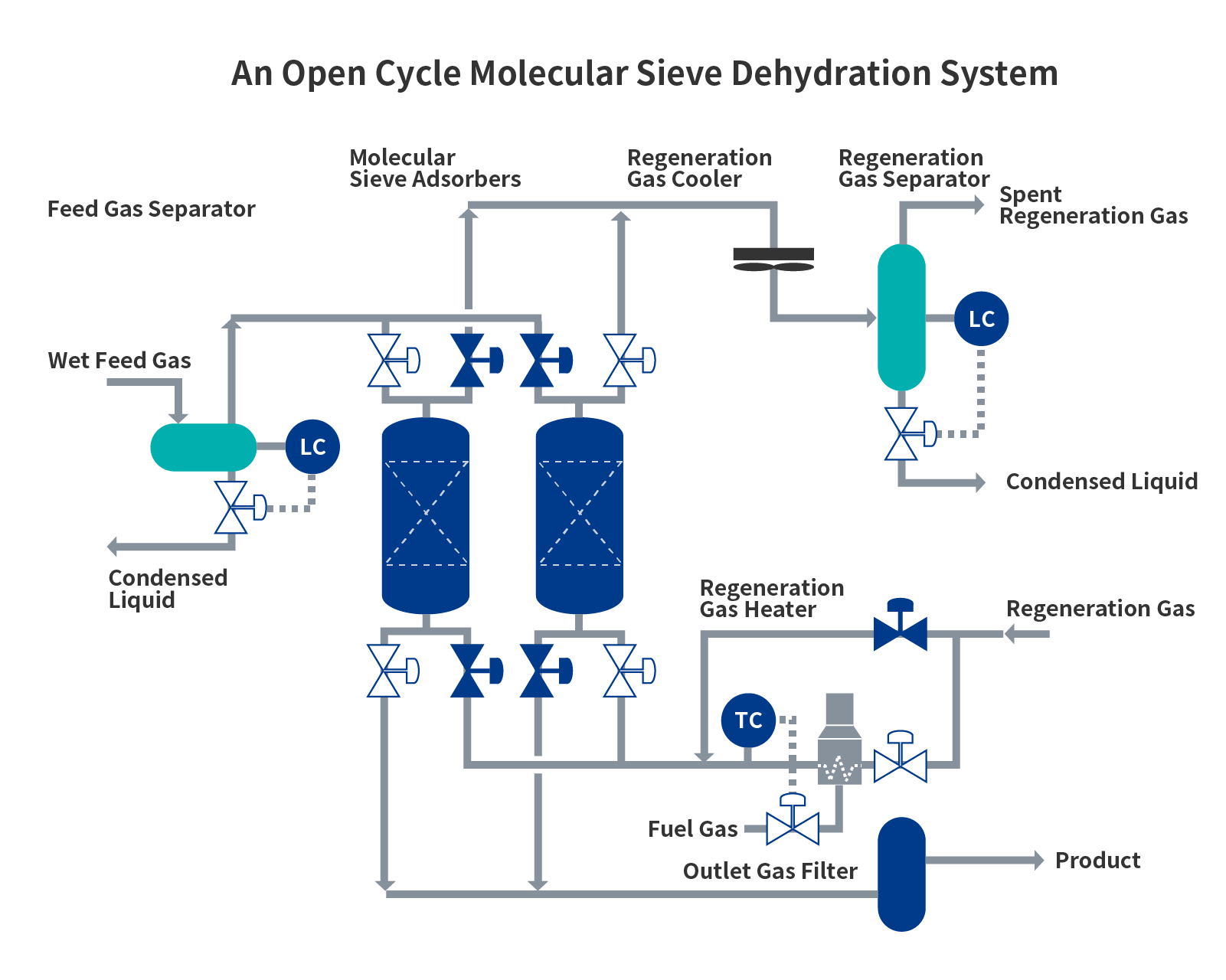
Dehydration and Organic Sulfur Removal Process Using Molecular Sieve (MS Treater)
Gas treated in the AGR contains water and an MS Treater uses a process based on the molecular sieve to remove and reduce the water content to a predetermined level. The molecular sieve predominantly consists of zeolite with a high adsorbing capacity to remove water from the gas. When mercaptans are removed, a different kind of zeolite is added. Fuel gas is heated for the regeneration (desorption) of the molecular sieve. For molecular sieves with a dehydration function, the spent regeneration gas is directly returned to the fuel gas system. A typical flow chart of the process is shown below. For molecular sieves that remove mercaptans, the spent regeneration gas is treated by a physical absorbent to remove mercaptan and then returned to the fuel gas. Mercaptans are regenerated in the regeneration plant and sent to the SRU as mercaptan acid gas. A typical physical absorbent process is the Selexol process of UOP with a similar flow chart to the AGR process.
A typical molecular sieve process, and its regeneration gas treatment, is the UOP MOLSIV process for which Chiyoda has unsurpassed design and construction experience.
Capability
- A characteristic of the molecular sieve (zeolite) is that it can adsorb different molecules depending on pore diameter size, allowing for selective adsorption.
- Due to the selective adsorption by the molecular sieve, it is possible to dehydrate without altering the composition of the product gas.
- The molecular sieve can be used for long periods through regeneration with high-temperature gas.
Applicable Range
The MS system can use feed gas including water, mercaptan and/or heavy hydrocarbon gas.
